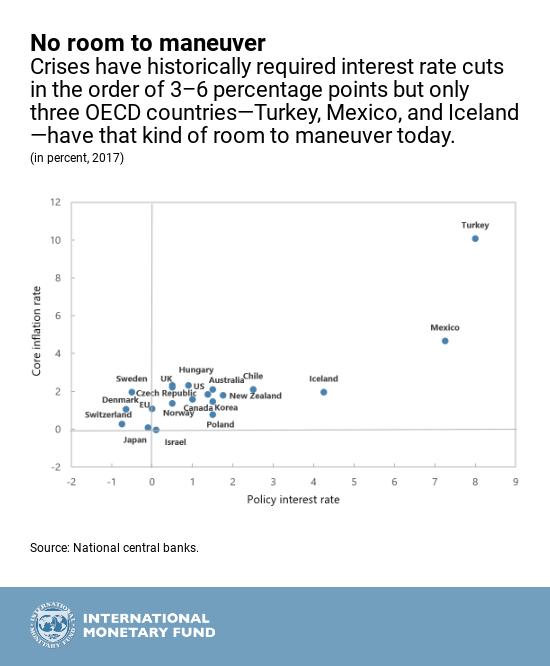
Many central banks reduced policy interest rates to zero during the global financial crisis to boost growth. Ten years later, interest rates remain low in most countries. While the global economy has been recovering, future downturns are inevitable. Severe recessions have historically required 3–6 percentage points cut in policy rates. If another crisis happens, few countries would have that kind of room for monetary policy to respond.
To get around this problem, a recent IMF staff study shows how central banks can set up a system that would make deeply negative interest rates a feasible option.
How low can you go?
In a cashless world, there would be no lower bound on interest rates. A central bank could reduce the policy rate from, say, 2 percent to minus 4 percent to counter a severe recession. The interest rate cut would transmit to bank deposits, loans, and bonds. Without cash, depositors would have to pay the negative interest rate to keep their money with the bank, making consumption and investment more attractive. This would jolt lending, boost demand, and stimulate the economy.
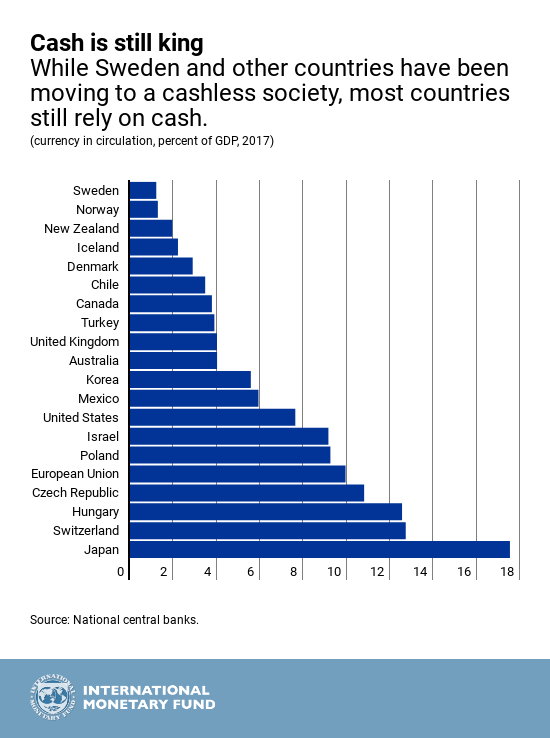
When cash is available, however, cutting rates significantly into negative territory becomes impossible. Cash has the same purchasing power as bank deposits, but at zero nominal interest. Moreover, it can be obtained in unlimited quantities in exchange for bank money. Therefore, instead of paying negative interest, one can simply hold cash at zero interest. Cash is a free option on zero interest, and acts as an interest rate floor.
Because of this floor, central banks have resorted to unconventional monetary policy measures. The euro area, Switzerland, Denmark, Sweden, and other economies have allowed interest rates to go slightly below zero, which has been possible because taking out cash in large quantities is inconvenient and costly (for example, storage and insurance fees). These policies have helped boost demand, but they cannot fully make up for lost policy space when interest rates are very low.
Breaking through zero
One option to break through the zero lower bound would be to phase out cash. But that is not straightforward. Cash continues to play a significant role in payments in many countries. To get around this problem, in a recent IMF staff study and previous research, we examine a proposal for central banks to make cash as costly as bank deposits with negative interest rates, thereby making deeply negative interest rates feasible while preserving the role of cash.
The proposal is for a central bank to divide the monetary base into two separate local currencies—cash and electronic money (e-money). E-money would be issued only electronically and would pay the policy rate of interest, and cash would have an exchange rate—the conversion rate—against e-money. This conversion rate is key to the proposal. When setting a negative interest rate on e-money, the central bank would let the conversion rate of cash in terms of e-money depreciate at the same rate as the negative interest rate on e-money. The value of cash would thereby fall in terms of e-money.
To illustrate, suppose your bank announced a negative 3 percent interest rate on your bank deposit of 100 dollars today. Suppose also that the central bank announced that cash-dollars would now become a separate currency that would depreciate against e-dollars by 3 percent per year. The conversion rate of cash-dollars into e-dollars would hence change from 1 to 0.97 over the year. After a year, there would be 97 e-dollars left in your bank account. If you instead took out 100 cash-dollars today and kept it safe at home for a year, exchanging it into e-money after that year would also yield 97 e-dollars.
At the same time, shops would start advertising prices in e-money and cash separately, just as shops in some small open economies already advertise prices both in domestic and in bordering foreign currencies. Cash would thereby be losing value both in terms of goods and in terms of e-money, and there would be no benefit to holding cash relative to bank deposits.
This dual local currency system would allow the central bank to implement as negative an interest rate as necessary for countering a recession, without triggering any large-scale substitutions into cash.
Pros and cons
While a dual currency system challenges our preconceptions about money, countries could implement the idea with relatively small changes to central bank operating frameworks. In comparison to alternative proposals, it would have the advantage of completely freeing monetary policy from the zero lower bound. Its introduction would reconfirm the central bank’s commitment to the inflation target, rather than raise doubts about it.
Still, implementing such a system is not without challenges. It would require important modifications of the financial and legal system. In particular, fundamental questions pertaining to monetary law would have to be addressed and consistency with the IMF’s legal framework would need to be ensured. Also, it would require an enormous communication effort.
The pros and cons of the system are country specific and should be carefully compared to other proposals, such as higher inflation targets, for increasing monetary policy space in a low-interest environment. We consider these issues, and more, in our research.